Algorithms and flow charts
Embedded software is made up of several functions that execute certain tasks. It's a good idea to construct an algorithm flow chart before writing any ASM or C code. Flow charts provide a visual representation of an algorithm's inner workings. Analyzing the algorithm and writing the code according to the diagram is easy.
If you think of a flowchart as a movie, an algorithm is the plot. In other words, the heart of a flowchart is an algorithm. In fact, there are several distinctions between algorithm and flowchart in the world of computer programming, including correctness, presentation, and public perception.
Assignment
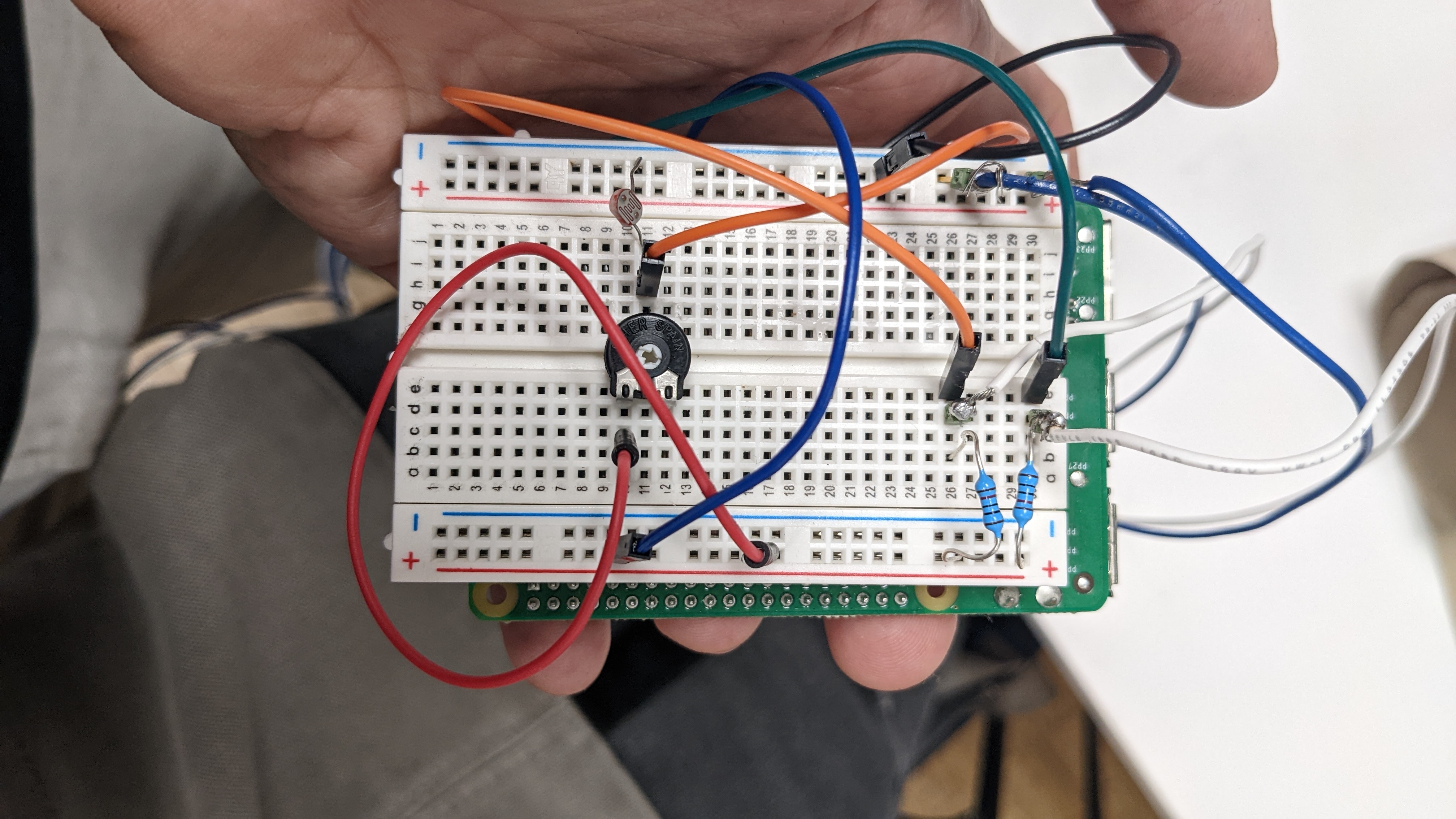
For the embedded programming assignment, I will be connecting a Raspberry Pi 2 Model B to a phototransistor (input), a couple buttons (input), and an audio device (output) through a breadboard.
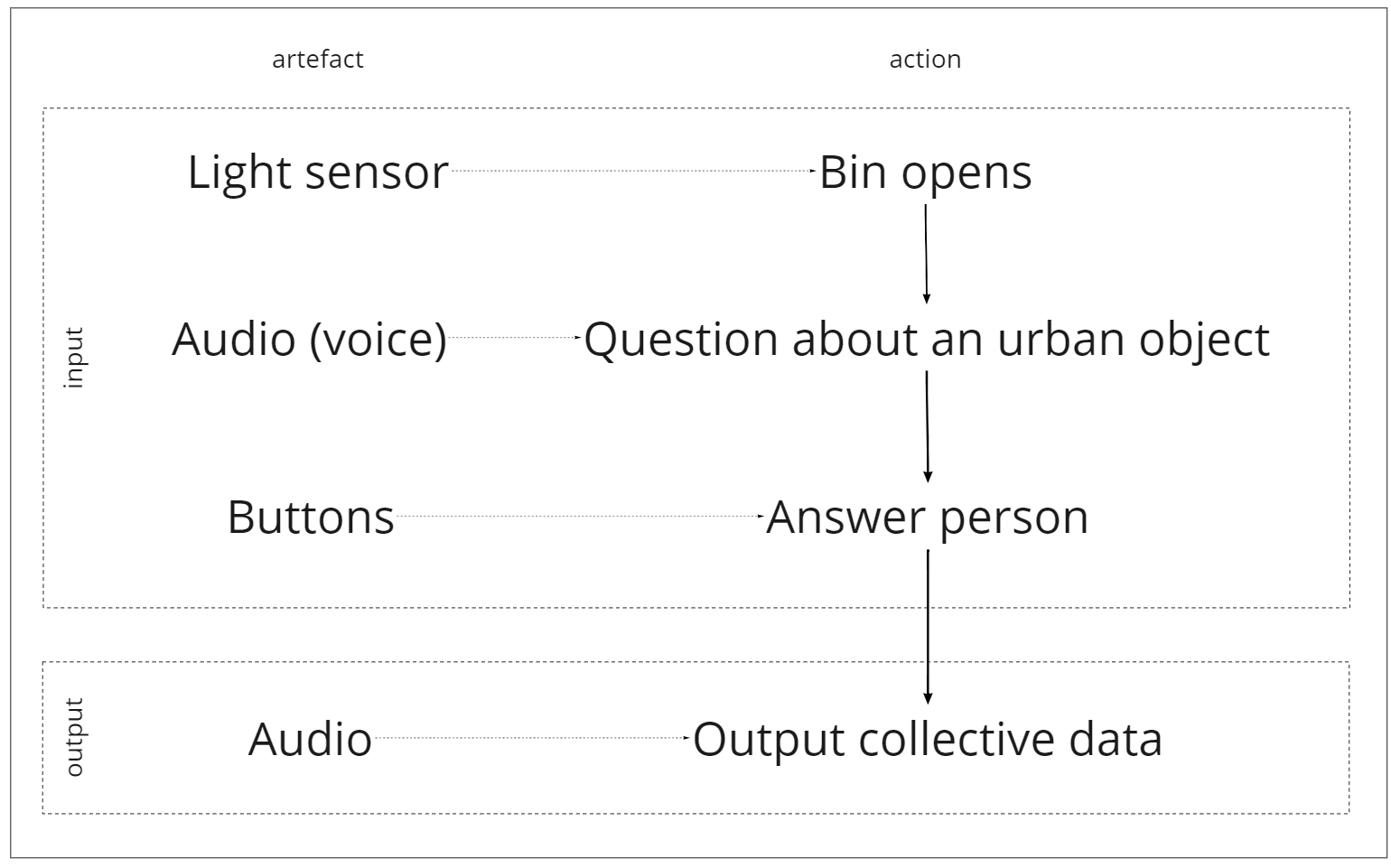
The main concept is a voting device that would collect (and reflect) the opinions of the community, basically anyone who will come to dispose of their trash. We chose a question that is general enough and would reflect the community's feelings, and at the same time provide the feedback back to the community.
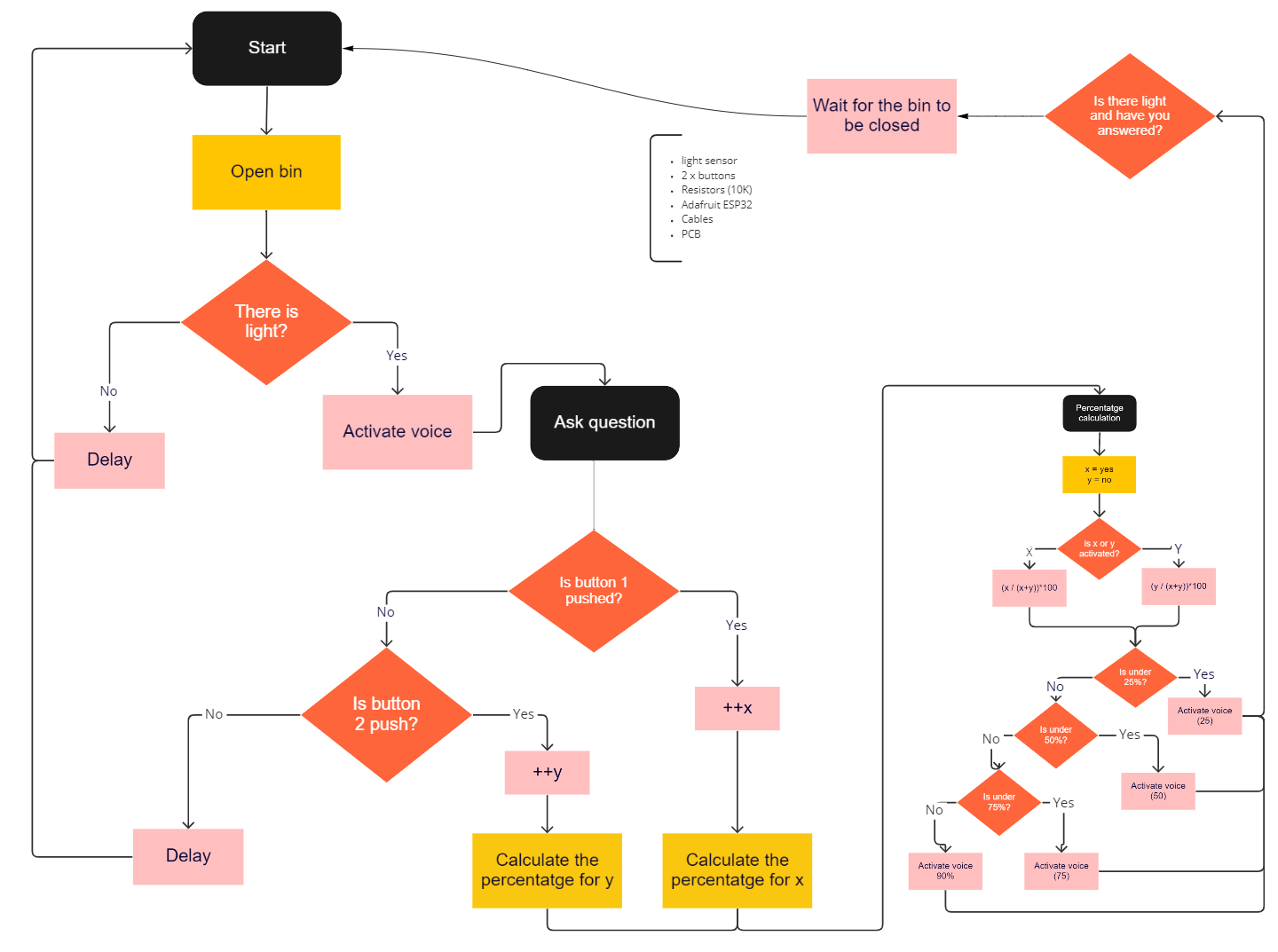
Flowchart
The flowchart describes:
The person opens the bin and that lets light through to the phototransistor. The device picks up the light and activates the voice which asks a question. The person then either responds by pushing button 1 or button 2. The information is sent to the computer and it calculates the percentage of x vs y based on the amount of answers received that day. The device then activates the audio once more to inform the user on the percentage of x or y that the other users have voted.

Coding on Python
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
import pygame
from datetime import datetime
from enum import Enum
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
GPIO.setup(4, GPIO.IN)
GPIO.setup(17, GPIO.IN)
GPIO.setup(27, GPIO.IN)
x = 0
y = 0
pygame.mixer.init()
# Possible states:
# lid_close
# playing_question
# waiting_answer
# playing_result
# idle
state = "lid_closed"
idle_timer = 0
waiting_answer_timer = 0
def ask_question_one():
global x
x = x + 1
result = round((x / (x+y))*100, 0)
play_result_audio(result)
print(result,f"% of yes -- X is {x} and Y is {y}")
with open('output.txt', 'a') as f:
f.write(f"{datetime.now().strftime('%d/%m/%Y - %H:%M:%S')} The user pressed Yes {x} times. Result is {result} \r\n")
def ask_question_two():
global y
y = y + 1
result = round((y / (x+y))*100, 0)
play_result_audio(result)
print(result, f"% of no -- X is {x} and Y is {y}")
with open('output.txt', 'a') as f:
f.write(f"{datetime.now().strftime('%d/%m/%Y - %H:%M:%S')} The user pressed No {y} times. Result is {result} \r\n")
def play_result_audio(result):
if result < 25:
#playsound('Bin02.mp3')
pygame.mixer.music.load("Bin02.mp3")
pygame.mixer.music.play(loops=1)
while pygame.mixer.music.get_busy() == True:
continue
print(f"play sound < 25 {result}")
elif result < 50:
#playsound('Bin03.mp3')
pygame.mixer.music.load("Bin03.mp3")
pygame.mixer.music.play(loops=1)
while pygame.mixer.music.get_busy() == True:
continue
print(f"play sound < 50 {result}")
elif result < 75:
#playsound('Bin04.mp3')
pygame.mixer.music.load("Bin04.mp3")
pygame.mixer.music.play(loops=1)
while pygame.mixer.music.get_busy() == True:
continue
print(f"play sound < 75 {result}")
else:
#playsound('Bin05.mp3')
pygame.mixer.music.load("Bin05.mp3")
pygame.mixer.music.play(loops=1)
while pygame.mixer.music.get_busy() == True:
continue
print(f"play sound < 100 {result}")
with open('output.txt', 'a') as f:
f.write(f"Beginning of reading {datetime.now().strftime('%d/%m/%Y - %H:%M:%S')} \r\n")
while True:
if state == "lid_closed":
print("[STATE] Lid is closed")
if GPIO.input(4) == 0:
state = "playing_question"
time.sleep(0.5)
elif state == "playing_question":
print("[STATE] Playing question")
pygame.mixer.music.load("Bin01.mp3")
pygame.mixer.music.play(loops=1)
while pygame.mixer.music.get_busy() == True:
continue
waiting_answer_timer = time.time()
state = "waiting_answer"
elif state == "waiting_answer":
print("[STATE] Waiting for an waiting_answer")
if GPIO.input(17) == 0:
print("Yes")
ask_question_one()
idle_timer = time.time()
state = "idle"
elif GPIO.input(27) == 0:
print("No")
ask_question_two()
idle_timer = time.time()
state = "idle"
if time.time() > waiting_answer_timer + 20:
state = "idle"
elif state == "idle":
print("[STATE] Idle")
if time.time() > idle_timer + 20:
if GPIO.input(4) == 0:
idle_timer = time.time()
if GPIO.input(4) == 1 and state != "waiting_answer" and state != "playing_result":
print("[STATE] Lid was closed")
state = "lid_closed"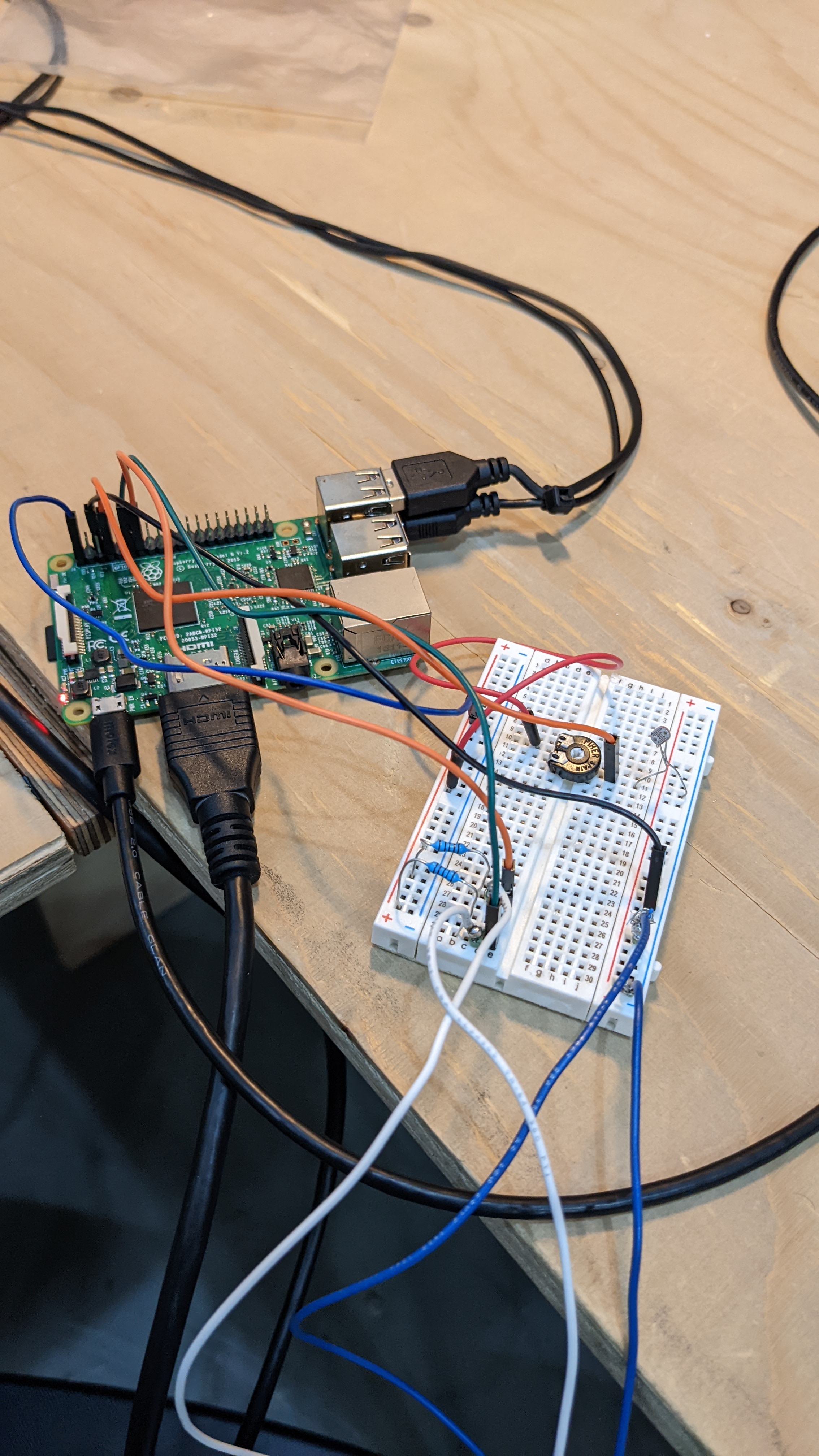
Final result